Designing a façade like a membrane

- Publish On 3 March 2021
- PCA-STREAM
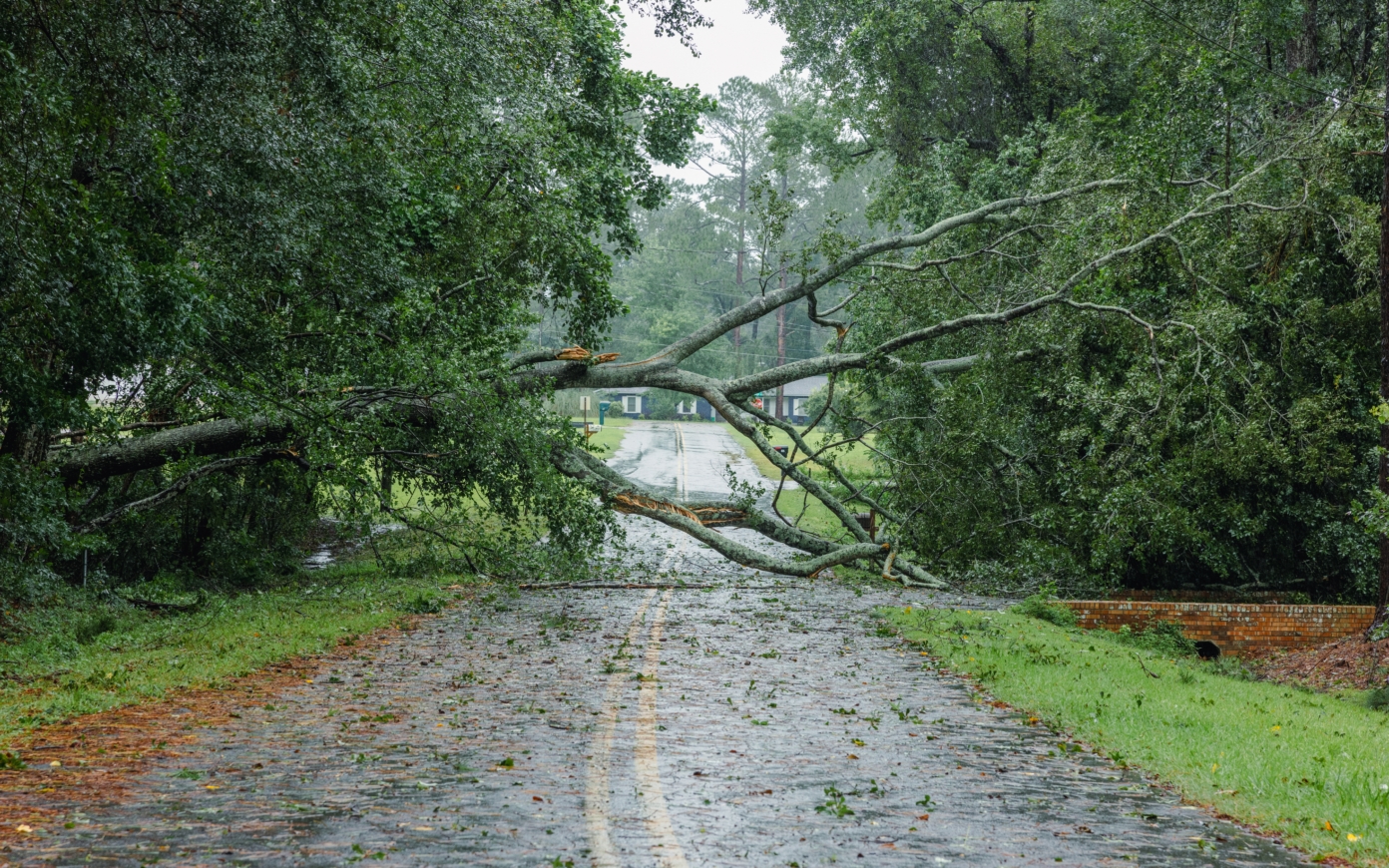
How can a building’s energy balance be maintained as a living organism would? The search for solutions has come to the forefront of contemporary concerns, with a view to finding a way for architecture to self-regulate its energy consumption based on uses and the fluctuations of the environment. One of the first surfaces concerned is the building’s façade, which is very similar to the material envelope of a body or the membrane of a cell: an interface between an interior that must be kept in balance and an exterior that is subject to variations the interior must be protected from. Much is at stake in the case of high-rise buildings. The double-tower high-rise “The Link,” which will emerge in La Défense in 2025, is typically subject to various constraints and challenges. To optimize user comfort, an ideal balance must be found between two paradoxical factors: the importance of daylighting and protection against exterior heat.
Increasing the Exchange Surface
In order to draw natural light deeper inside the building, the archetypal form of the high-rise tower is called into question. The Link is made up of two cores connected in a figure-of-eight shape, thereby increasing the exchange surface with the exterior and leading to larger surfaces being exposed to direct sunlight instead of having blind elevator shafts at their core, as is typical in high-rises.
An architectural decision was made to open up as many perspectives as possible on the exceptional landscapes of the Seine hillsides, the Bois de Boulogne Park, the rooftops of Paris, and the La Défense skyline, thanks to full-height glazing.
This vast transparent surface, with 360 degrees of exposure to the sun, must however allow for user thermal comfort, as well as reduced energy use. How can natural light then be allowed in but not the heat, all the while preserving the views of the distant horizon? Tinted glass has run its course—it alters the perception of the landscape and generates significant energy consumption as workspaces must be artificially lit even during the daytime.

A Façade with Variable Typologies
Based on the interpretation of a solar simulation, PCA-STREAM’s architectural teams, in partnership with the engineering consultancy VS-A, have worked on adapting the façade to its environmental context. They have developed an envelope with variable typologies to address different constraints, with a single skin on the north side and a double skin on the south side, which has the most sun exposure.