Encouraging the matter

- Publish On 18 November 2017
- Michel Blazy
- 9 minutes
Involving the living directly in artwork opens up creative opportunities that question the status of the author and of the artist. For Michel Blazy, if the figure of man seems to become discreet or even disappear from his work, that of the artist remains quite present. It is less a matter of ceding power to the living, of “allowing it to happen,” at the risk of nothing happening, than of creating the conditions for emergence, of encouraging matter in the manner of a gardener. The artist observes and seeks to understand the living in order to favor its development, in such a way that the form self-generates. In this way, he explores the conditions for a domestication of the living that are symbiotic rather than exploitative. The formal fascination for the living underpins his thinking about the intelligence of survival and the frontiers between the inert and the organic. Living and art have in common the fact that they both escape understanding to some extent; the artist is not trying to deliver an unequivocal message but to share an experience—the struggle with matter in the studio—and to provoke the complexity of encounters.
Ethics of collaboration with the living
By yielding formal power on your artworks to the living world, your work questions the nature of authorship; does the decline of the figure of man and the artist in this “laissez faire” approach confer a special status to the mice, snails, birds, mushrooms, or protocellular micro-organisms that compose the artworks?
In reality, I do not leave it entirely to them because this could result in nothing happening at all, which would bore viewers. My philosophy is more about nurturing matter, just like a gardener who would take the necessary measures to ensure that things actually happen, even if they arise from forces far beyond their understanding. Gardeners water or mulch the soil but are not the ones that actually make plants grow; they provide the conditions for the establishment of living systems. Obviously, I am not referring to intensive agriculture or weed control, but rather to the idea of the absence of an obligation to achieve results when dealing with things that cannot be brought under complete control. I am not trying to prevail over things, nor to bend them to my will, but rather to observe them, to understand how they function and what their needs are to ensure that they flourish. I do not know in advance what will happen when I conduct experiments in my workshop and this constant surprise is precisely what I am interested in. I provide the necessary conditions for the form to self-generate, which leads me to replicate things that could happen without me. The human figure fades away and keeps a low profile, but not that of the artist. There is no doubt that I am the artist, and not the mice or the mold, although the result does reflect a form of collaboration.
It is indeed the result of joint work, of a partnership, but would you refer to this as domestication?
Yes, this is domestication, with its risks and rewards. Things can indeed run out of hand in the sense that domestication isn’t always a success. There were instances when I was totally overwhelmed by insects, smells, or mold during exhibitions. The idea of domestication is somewhat ambiguous—dogs probably sought out humans out of their own interest, for example. I even sometimes wonder whether the dog or its master is the true owner, especially when I witness scenes where a pet is sitting on the laps of their master and eating from their plate or when they share the same bed. Dogs exert considerable pressure during mealtime and oftentimes, the pet is the one that requests to be served. But there are all kinds of domestications. Some fall under outright exploitation and can be equated to a form of parasitization, sometimes even leading to the death of the animal. In a sense, this is fairly representative of humankind’s general attitude toward its environment.
Other forms of domestication are more akin to symbiosis. The Maasai cut a small slit in the jugular vein of their cows to drink their blood. The animals thus remain alive, their blood is renewed and the Maasai get the protein and the liquid they need. The end result is that the cows are treated well, in spite of this bloodletting, because the Maasai are well aware of what the cows couldn’t withstand; the Maasai respect them, feed them, protect them from predators, and so on. Choosing between these two approaches is a political choice. Personally, I view domestication as enlightened self-interest. In my work Lâcher d’escargots sur moquette marron (Snail Release on Brown Carpeting), I use their slime to produce a kind of paint, for which they receive beer, which they are mad about. I offer them some good time in exchange for a small performance, after which I release them back into the wild. I hope this domestication isn’t too traumatic.
Likewise, the exhibit Table auto-nettoyante (Self-Cleaning Table) contains the idea of “commensality,” which is linked with the idea of domestication. I offer a haven for ants in the legs of the table as well as food—the crumbs generated by the meal—in exchange for a cleaning service. There is a shared interest. This work puts into perspective the issue of cohabitation as well as the way in which we could share the same space so that there may be something for everyone. We feed on living beings, both animals and plants, and are therefore intimately connected to the living. Admittedly, all living creatures aim to self-preserve and to self-perpetuate, to survive as long as they can, yet asking ourselves how to intelligently deal with other living things isn’t a moral issue but is first and foremost common sense.

In my work Circuit fermé (Closed Circuit)Presented as part of Le Grand Restaurant, Blazy’s solo exhibition at Le Plateau, one of the Fonds régional d’art contemporain (FRAC) Île-de-France’s two exhibition spaces., I also touch on predation. A number of people are kept in a glass room where they eat meat and are bitten by mosquitoes. This covers the idea of “giving back.” All my work relates to this relativity of being, to the investigation of the notions of fading away and lack of control, because I puzzle over the power we wrest from the living. All the more so given that we wield that power in an increasingly alarming way, even though we are only one link in the chain of living things. Our desire to protect the planet is quite symptomatic of this extreme pride. The planet doesn’t give a damn about human beings; it started out without us and will carry on likewise. The living has absolutely no need for our protection. Humankind is first and foremost a danger to itself.
Considering the living limits
Is it a form of relativism to attribute some importance to “useless and disregarded presences” that are regarded as waste or refuse?
I must admit that my work with mold finds its roots in a purely plastic fascination. If you take the time to observe mold, you’ll notice how gorgeous it is: it is fluffy, forms beautiful circles, and the shapes and colors are constantly changing. Mold is nevertheless shunned because it is ingrained in our collective psyche with all sorts of concepts relating to hygiene, death, and control and thus brings together a great number of fears and anxieties. I am involved with this material because it is alive and therefore possesses, like all living beings, a form of intelligence that it puts to use for its survival.
The fact that a germ must move around, find food for itself, and reach compromises with its kind in order to share a constrained space reminds us that all living individuals contend with the same issues, though the solutions may take on many different forms. We are all faced with this issue of self-preservation of the living.
In your piece, Les Nouvelles amibes domestiques (New Domestic Amoebas), you make invisible existences visible and blur the common understanding of what a “living” thing is. How do you differentiate the inert and the organic?
I do not differentiate inert things from living things, and organic matter from what isn’t. In nature, it all ends up being mixed together; and that is precisely the problem. Whatever the material, it interacts with its environment and ends up becoming part of the great planetary body. Although plastics dumped at sea decay and disappear out of sight, fish ingest the particulates and eventually end up being eaten themselves. All matter thus blends together. There is no matter that I don’t view as being alive. I find it hard to understand the boundary that we place between the inert and the organic when everything is constantly changing over time. It’s just like life and death, like movement and stillness. Things are in constant motion around us—the Earth that is rotating around its own axis, a child or a plant that is growing, a micro-organism that is “hunting”—but we do not necessarily notice that. It’s just a matter of perception because how we see things is determined by our time span. If we lived longer than mountains and could perceive their movements, we would maybe consider them more as living things. I am interested in slowness and in movements at the threshold of perception, those we have to get away from for some time to be able to start noticing them.
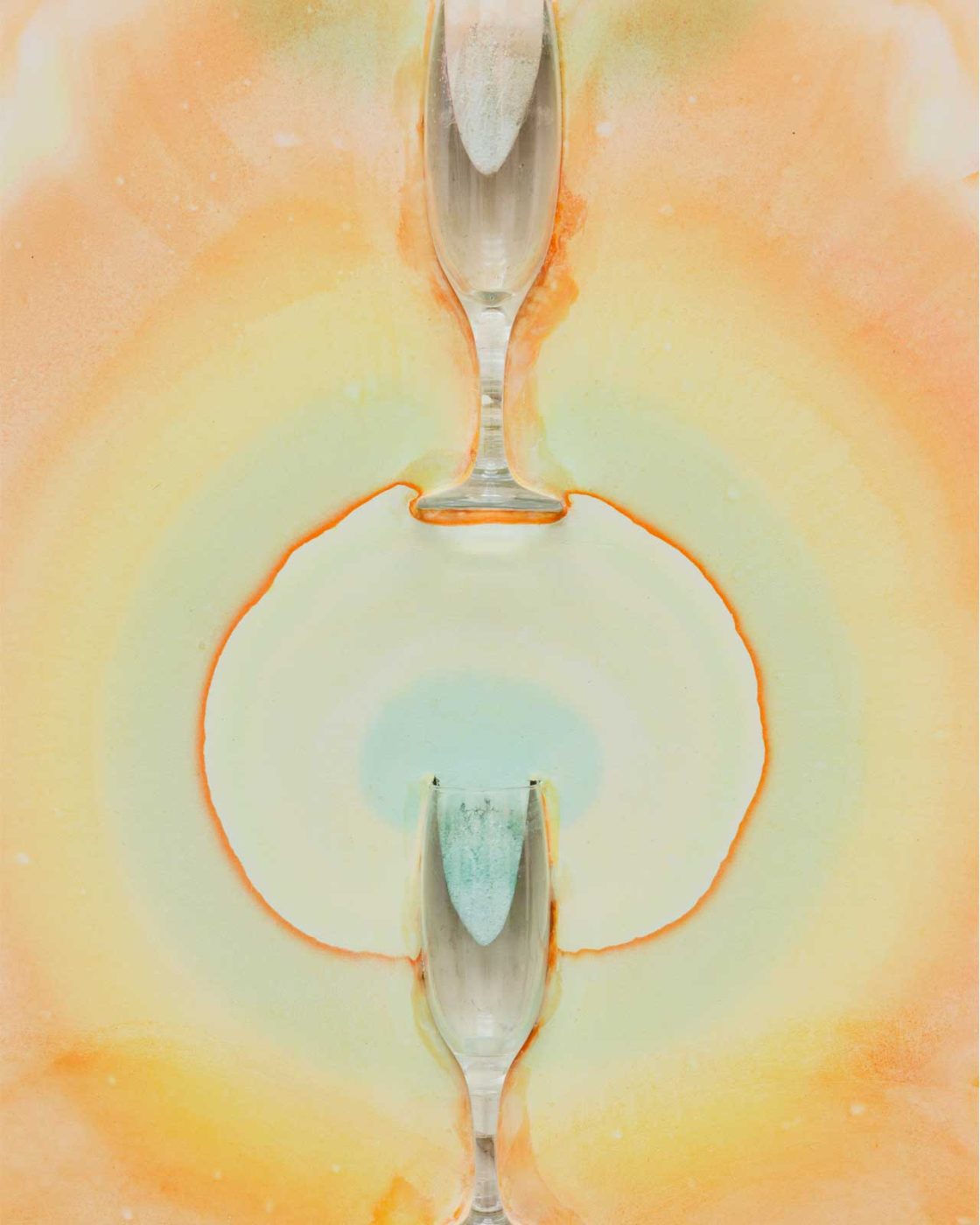


In the same way, considering that my artworks grow or decay is a matter of perspective. In 1997, I had planted bags of lentils for an exhibition at the Musée d’Art Moderne de la ville de Paris, thinking that I would change them when they spoiled. The lentils did indeed spoil and gave place to mold, fruit flies, and their predators, spiders. Although the primary work had decayed, it produced ten times more life than the plain green lentils. I therefore left this apparently dead matter in place. Life feeds on death and beyond our individual identities, I view the living as one large clump of matter that evolves, changes shapes, and feeds on its own death.
People who are concerned with their environment and other forms of existence generally express views that are close to animism. They refer to a certain spirituality, whereas you primarily consider matter, the concrete, and textual content, thus opting for a rather pragmatic approach. Do you sometimes consider the intangibles in the living world?
I don’t believe I am an animist but that does not mean, however, that I am materialistic. I believe in invisible forces but above all I believe in mystery. Matter, the concrete, and textual content do not reduce the mystery in any way. I’d even go so far as to say that they set the stage for it. There is a part of the living, and a part of art, that eludes our understanding, and this is the primary reason why I am attracted to both these things.
Can we conceiving the artwork as a pet?
Do the buyers of your living pieces become their masters, just as they would be for a pet? Do they have a moral obligation to care for these micro-organisms?
Nouvelles amibes domestiques (New Domestic Amoebas) is a reference to the French acronym for exotic pets. My interest has turned to how the physical and subjective relationship we may have with a pet can be transposed to an artwork. I truly believe that art’s sole interest is to address intimacy. I started working on this subject in a rather intuitive way, perhaps because I felt a certain degree of morbidity in the exhibitions that only presented the remnants of a gesture or an intention. Since then, I try to arouse an affective response to something that is going on. What matters for me, and what I believe makes a moment important, is its scarcity, the fact that we find ourselves in front of something that we feel will not last. I do not only aim to show the process—given that any artwork results from it—but also things in the making.
Too many art collectors are driven to purchase artworks by belongingness and recognition, or see it as an investment, given that artworks are tax-exempt. Ninety percent of the art market occurs outside of an intimate relationship with the artwork though it is, I believe, the only one that really matters. The emotional connection that arises between the buyer and the artwork is what I am interested in, this beautiful melody that uplifts us and stirs up intimate recollections.
Regarding the physical outcome of the amoebas, bear in mind that these are organisms which are endowed with mouths they use to feed. But the fate of the artwork is at the discretion of the collector, who may continue to feed the amoebas or otherwise. Deprived of a water supply, these animals remain “dormant” and only “come back to life” once their environmental conditions are restored.
Either way, the artwork is destined to change. I use food coloring that is similar to the dyes used for microscopy to dye the amoebas that are present in the water. If the plaster substrate that serves as an exoskeleton is frequently sprinkled with water, the colorful halo that reveals the local accumulation of amoebas will have a deeper color. If, on the other hand, nothing is done, the colors of the UV-sensitive dyes will fade away, reflecting the passage of time. To prevent the art work from withering away, it should therefore be fed from time to time; I do not require a protocol of two daily meals to be observed, however.
What message are you trying to convey through such a work?
My work does not aim to speak up against an improper conduct or to convey a message. I am simply trying to find a suitable place for myself. I do not know what I am trying to expressand am discovering it as I go along. The artworks start taking on a life of their own and expressing things that didn’t even occur to me. I do not view art as a medium to deliver a message; this has more to do with PR and media coverage. For me, art is an encounter, with all the complexity that this encompasses. An encounter teaches a lot more than a message: it’s inexhaustible. This is what I aim to bring about, true encounters of the kind I have sometimes had with some artworks. These are life-changing moments; they follow you around and string along like a small whisper in your head. On the contrary, advertising messages are univocal.
When I make an artwork, I am completely immersed in matter and in what I am making, which implies a form of encounter. Exhibiting the artwork is nothing more than conveying what I experienced in the workshop to an audience. I make my own personal encounter available to the public, hoping that the spectators will also experience it. I am therefore a matchmaker, so to speak.