Bringing together an architectural project and a collection project
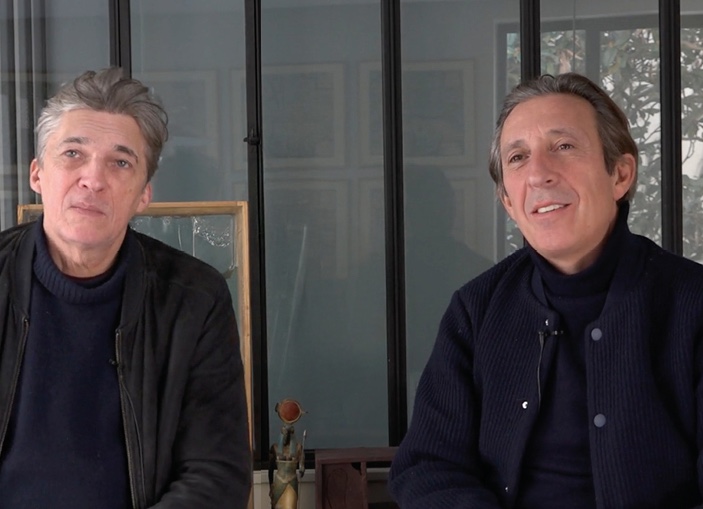
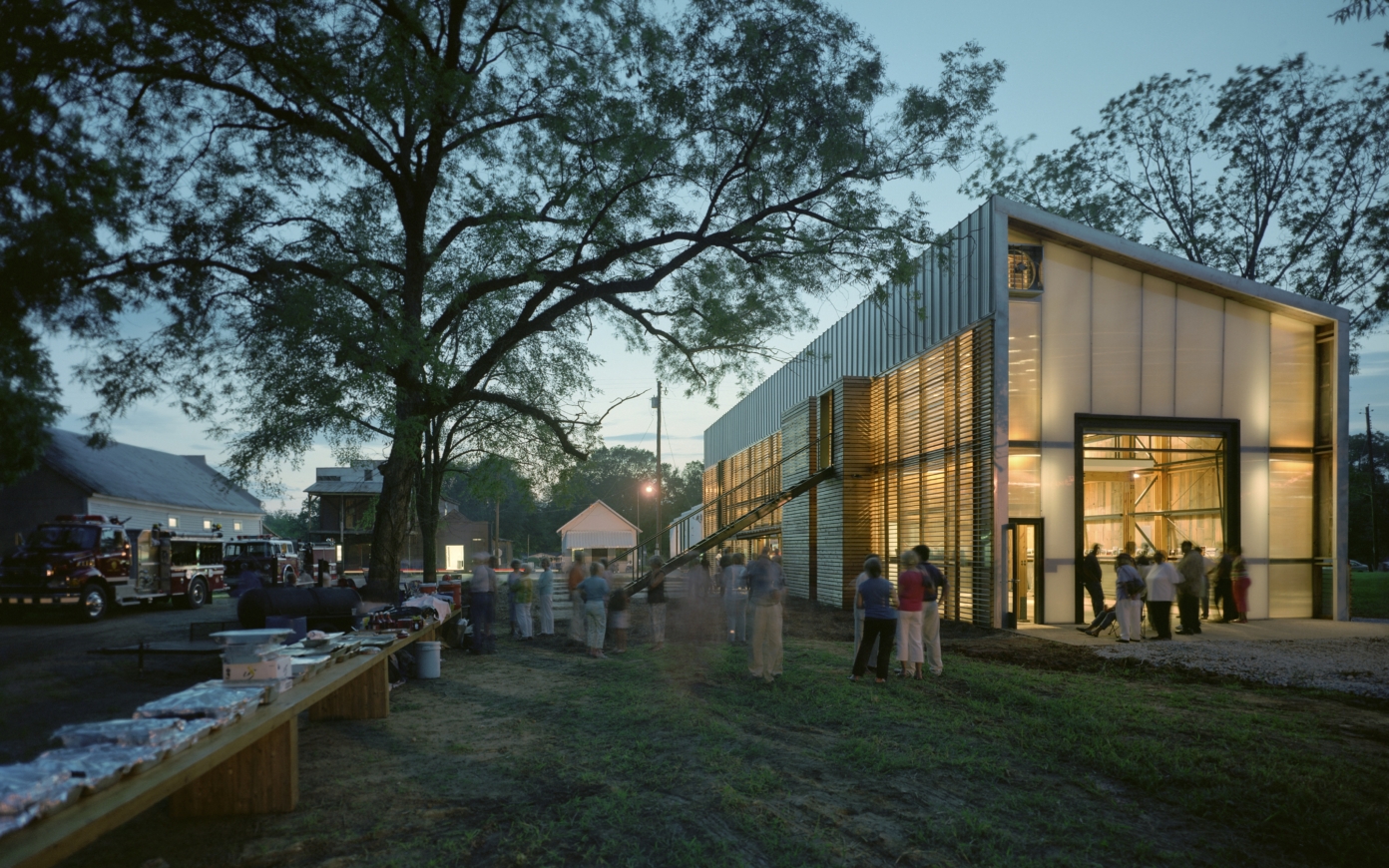
L’agence PCA-STREAM dirigée par l’architecte Philippe Chiambaretta a signé en 2006 le projet de réhabilitation d’un immeuble tertiaire destiné à accueillir le tout nouveau Centre d’Art Contemporain de Kiyv. Le projet architectural s’est construit en parallèle du positionnement éditorial et de la constitution de la collection, en collaboration étroite avec le mécène du projet Viktor Pinchuk et le curateur Nicolas Bourriaud. Retour sur la genèse de ce projet ambitieux, destiné à ouvrir l’Ukraine sur le Monde.