Stone

- Publish On 2 May 2024
- Elisabeth Bouchaud, Cyril Pressacco, Denis Macrez, Ana Hedan, Paul Vergonjeanne
- 109 minutes
Discover the inaugural lecture of the “Alma Matter” series! In a world where the myth of abundance is collapsing, this series of lectures looks at what matter really has to offer. Actors, professions, economies, temporalities, geopolitics: how do contemporary issues of creation take shape through those of matter? Each talk focuses on a particular material, and brings together its stakeholders in a dialogue.
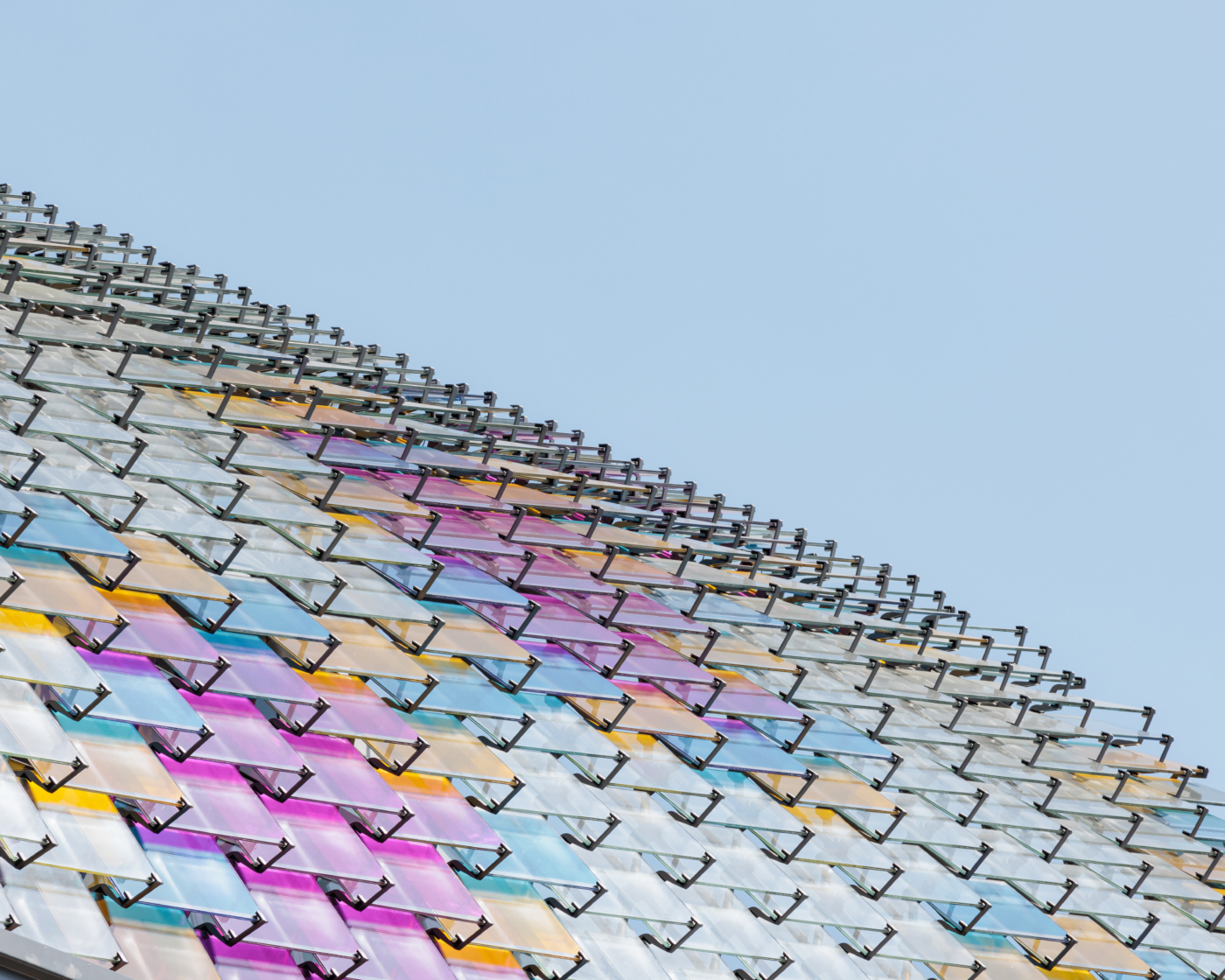
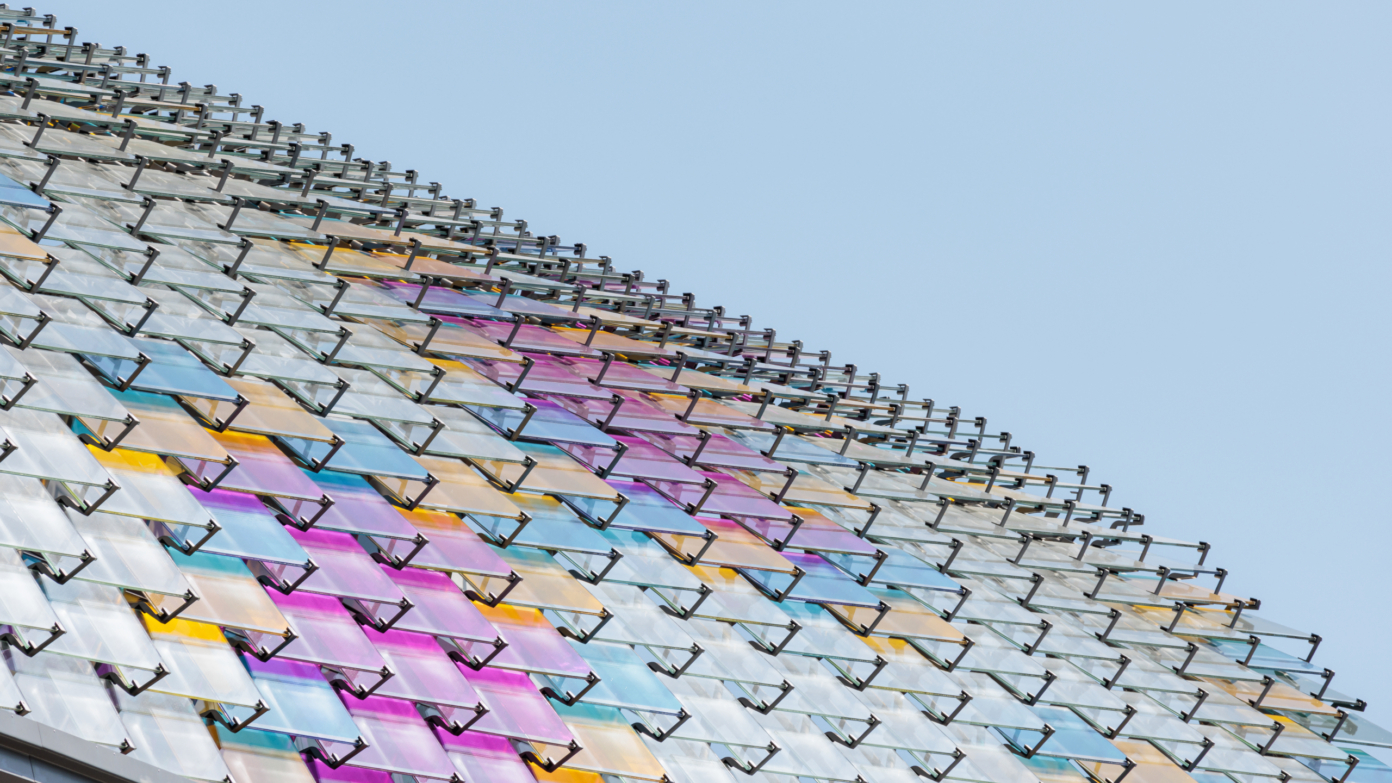
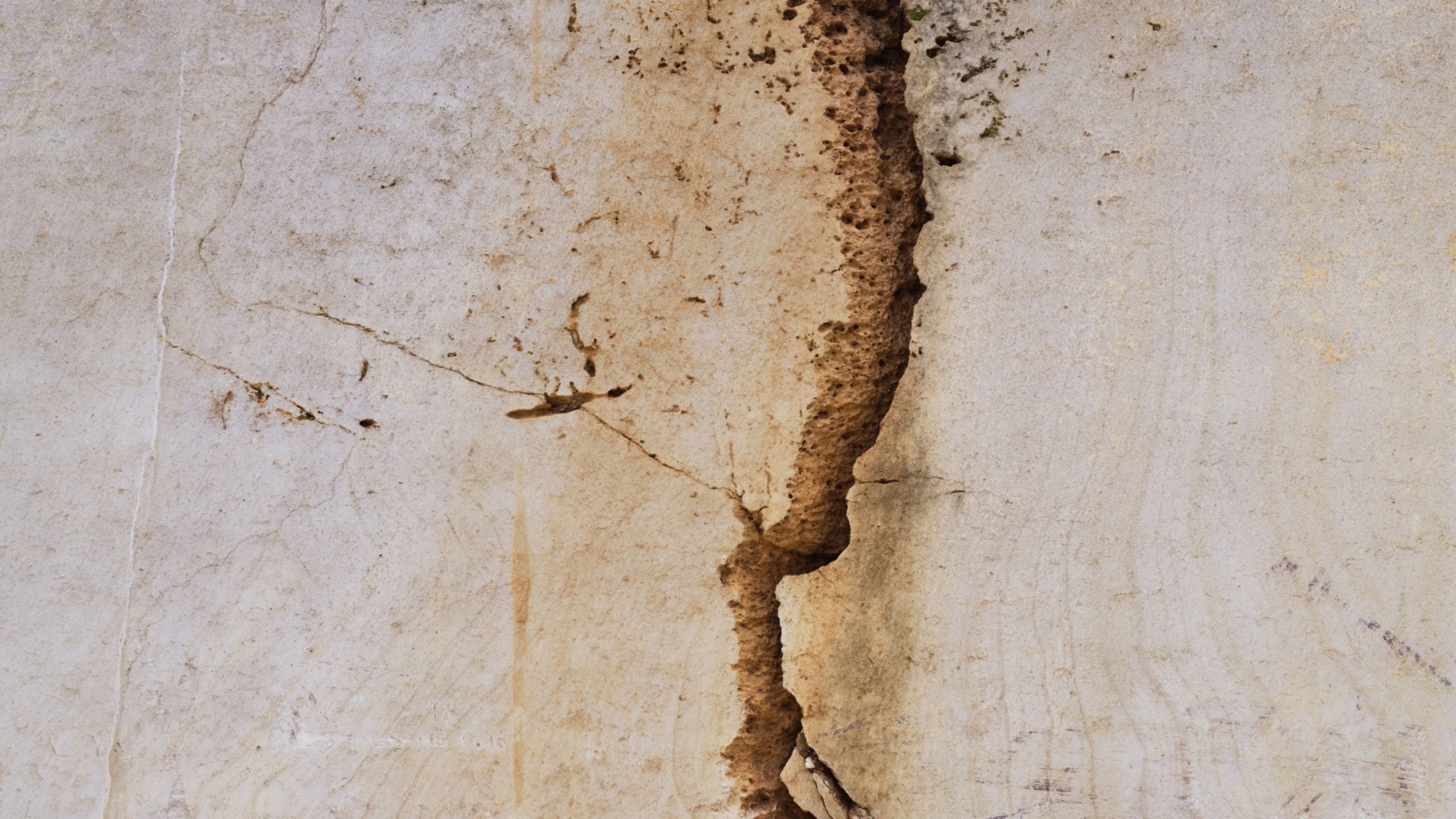
The use of stone in construction declined during the twentieth century. Today, its return is acclaimed for its qualities: inertia, durability, low-emission processing, local presence… but what techniques and applications will be used in 2024?
As part of the City Metabolism Chair supported by the Université Paris Sciences & Lettres.